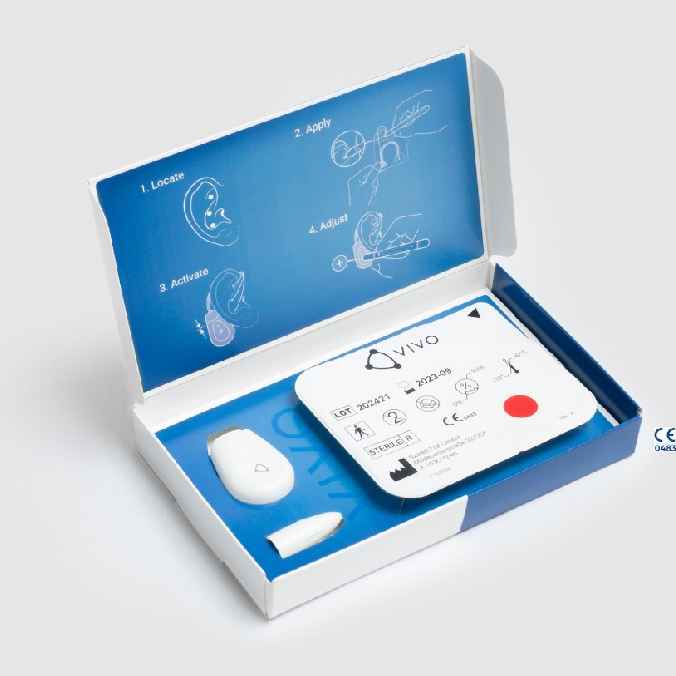
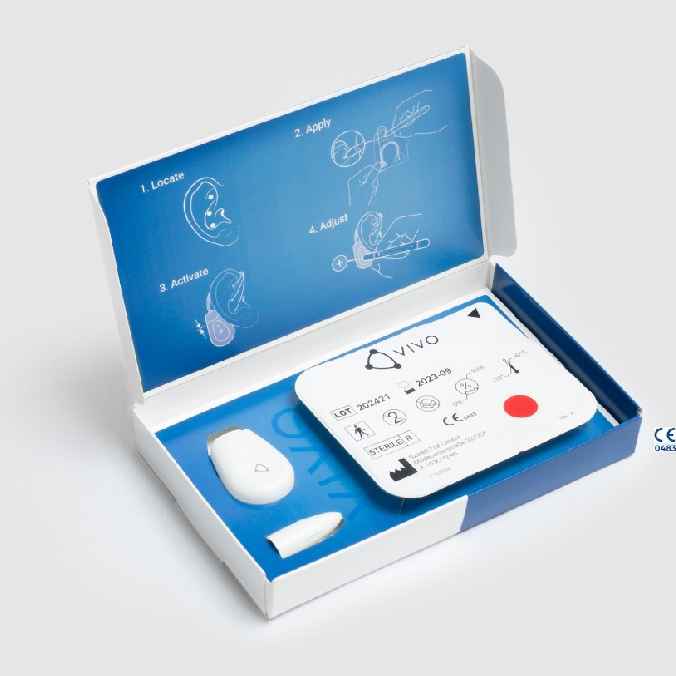
Description
The vagus nerve plays an important role in the autonomic nervous system
of the human body and in the processing of pain. By stimulating the auricular
vagus nerve with electrical impulses, it is now hypothesised that
- pain signals are blocked (gating),
- inhibiting pain pathways are activated,
- the body’s own opiates (endorphins, enkephalins, etc.) are released,
- the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway is activated and an
anti-inflammatory effect is triggered, - the sympathovagal balance is improved.